The World Health Organisation released the latest data about the Novel Coronavirus, which originated in Wuhan, China
Situation update:
• A total of 1,320 confirmed cases have been reported for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) globally;
• Of the 1,320 cases reported, 1,297 cases were reported from China, including Hong Kong SAR (5
confirmed cases), Macau SAR (2 confirmed cases) and Taipei (3 confirmed cases).
• A total of 1,965 suspected cases have been reported from 20 Chinese provinces, regions and cities
(excluding Hong Kong SAR, Macau SAR and Taipei).
• Twenty-three confirmed cases have been reported outside of China in nine countries (see table-
1).
• Of these 23 confirmed cases, 21 had travel history to Wuhan City, China; one case in Australia had
direct contact with a confirmed case from Wuhan while in China; and one confirmed case in Viet
Nam had no travel history to any part of China as mentioned in situation report published on 24
January. According to preliminary investigations, this constitutes an instance of human to human
transmission within a family.
• Of the 1,287 confirmed cases (excluding Hong Kong SAR, Macau SAR and Taipei), 237 cases have
been reported as severely ill2 .
• Forty-one deaths have been reported to date (39 deaths in Hubei province, one death in Hebei
province and one in Heilongjiang province).
• On 25 January 2020, the number of reported confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV has increased by 474
cases since the last situation report published on 24 January 2020.
WHO’s assessment of the risk of this event has not changed since the last update (22 Jan): very high
in China, high at the regional level and moderate at the global level.
1
The situation report includes information reported to WHO Geneva by 10 AM CET
2
Severe illness: According to any of the following criteria:
(1) shortness of breath; (2) respiratory rate more than 30 bpm; (3) hypoxemia; (4) chest X-ray with multi-lobar infiltrates or
pulmonary infiltration progressed more than 50% within 24 – 48 hours.
1
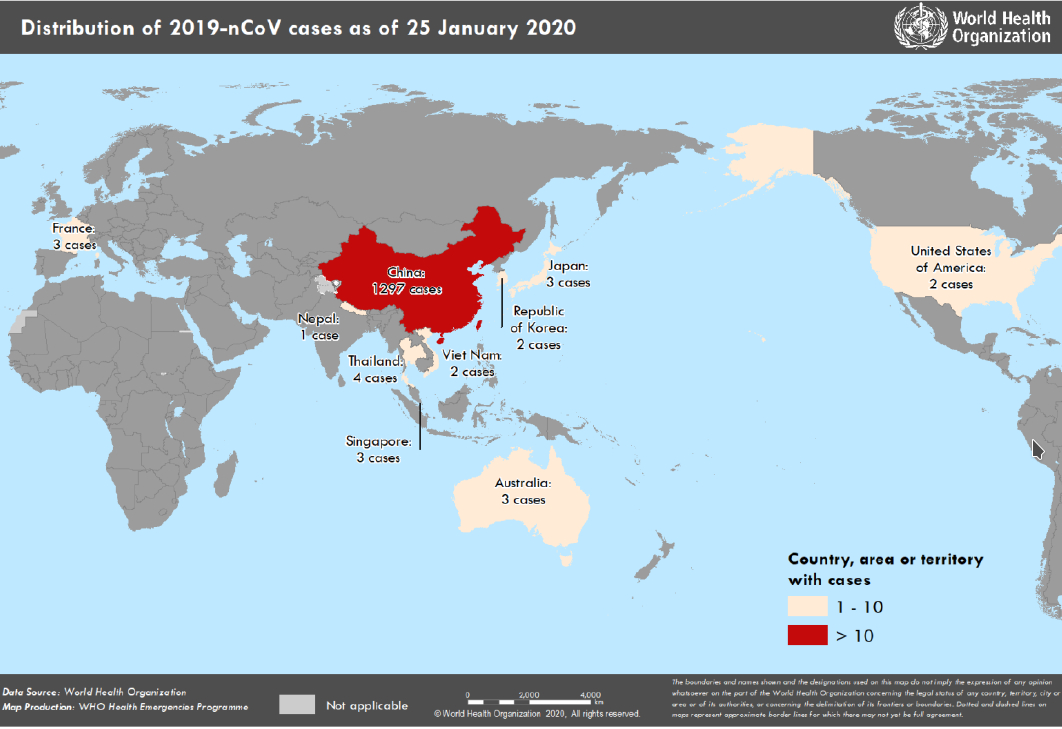
Figure 1. Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV, 25 January
2020
2
I. SURVEILLANCE
Reported incidence of confirmed 2019-nCoV cases
Table 1. Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV, 25 January
2020
Confirmed
WHO Regional Office Country/Territory/Area
Cases
China* Total 1297*
Japan 3
Republic of Korea 2
WHO WPRO Region
Viet Nam 2
Republic of Singapore 3
Australia 3
Thailand 4
WHO SEARO Region Federal Democratic Republic of
1
Nepal
WHO PAHO Region United States of America 2
WHO EURO Region French Republic 3
Total Confirmed
Total 1320
cases
*Confirmed cases in China include cases confirmed in Hong Kong SAR (5 confirmed cases), Macau SAR (2 confirmed cases)
and Taipei (3 confirmed cases).
3
II. PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE:
WHO:
• WHO has published an updated advice for international traffic in relation to the outbreak of
the novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV.
• WHO has been in regular and direct contact with Member States where cases have been
reported. WHO is also informing other countries about the situation and providing support
as requested.
• On 2 January, the incident management system was activated across the three levels of
WHO (country office, regional office and headquarters).
• Developed the surveillance case definitions and reporting forms for human infection with
2019-nCoV and is updating it as the new information becomes available.
• Developed interim guidance for laboratory diagnosis, clinical management, infection
prevention and control in health care settings, home care for patients with suspected novel
coronavirus , risk communication and community engagement.
• Prepared disease commodity package for supplies necessary in identification and
management of confirmed patients.
• Provided recommendations to reduce risk of transmission from animals to humans.
• Utilizing global expert networks and partnerships for laboratory, infection prevention and
control, clinical management and mathematical modelling.
• Activation of R&D blueprint to accelerate diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
• WHO is working with our networks of researchers and other experts to coordinate global
work on surveillance, epidemiology, modelling, diagnostics, clinical care and treatment, and
other ways to identify, manage the disease and limit onward transmission. WHO has issued
interim guidance for countries, updated to take into account the current situation.
The strategic objectives of the response are to interrupt the transmission of the virus from one
person to another in China, to prevent exportation of cases from China to other countries and
territories, and to prevent further transmission from exported case if they were to happen. This can
be achieved through a combination of public health measures, such as rapid identification, diagnosis
and management of the cases, identification and follow up of the contacts, infection prevention and
control in healthcare settings, implementation of health measures for travellers, awareness raising
in the population, risk communication.
During previous outbreaks due to other coronavirus (Middle-East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
and the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)), human to human transmission occurred
through droplets, contact and fomites, suggesting that the transmission mode of the 2019-nCoV
can be similar. The basic principles to reduce the general risk of transmission of acute respiratory
infections:
• Avoiding close contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections.
• Frequent hand-washing, especially after direct contact with ill people or their environment.
4
• Avoiding unprotected contact with farm or wild animals.
• People with symptoms of acute respiratory infection should practice cough etiquette (maintain
distance, cover coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues or clothing, and wash hands).
• Within healthcare facilities, enhance standard infection prevention and control practices in
hospitals, especially in emergency departments.
• WHO does not recommend any specific health measures for travelers. In case of symptoms
suggestive of respiratory illness either during or after travel, the travelers are encouraged to seek
medical attention and share their travel history with their health care provider. Travel guidance
has been updated.
5
III. COUNTRY RESPONSE:
China:
• Public education on disease prevention and environmental hygiene further strengthened in
public places across the city, farmers’ markets in particular. As of 23 January, the National
Health Commission revised protection standards and specifications for medical workers and
strengthened prevention and control measures against 2019-nCoV in hospitals.
• National authorities are conducting active case finding in all provinces.
• Search expanded for additional cases within and outside of Wuhan.
• Active / retroactive case finding in medical institutions in Wuhan.
• The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was closed on 1 January 2020 for
environmental sanitation and disinfection. Market inspection in expansion to other markets.
Australia:
• Updated General Physicians, pharmacists, emergency departments, and the broader health
system on the situation as it evolves to enable possible cases to be rapidly identified,
diagnosed and managed.
• Developed diagnostic tests through the Public Health laboratories to rapidly diagnose cases
• Supported the Commonwealth to provide advice and assess travellers for illness on the
direct flight from Wuhan to Sydney on 23 January.
• Providing regular updates to the community, through media briefings, media release and
social media including in Mandarin.
• Infection with 2019-nCoV is now notifiable under the New South Wales Public Health Act
2010, so doctors and pathology laboratories are required to notify NSW Health of all people
suspected to have this infection.
6
Resources:
• Technical interim guidance for novel coronavirus, WHO:
https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus
• WHO travel advice for international travel and trade in relation to the outbreak of the novel
coronavirus 2019-nCoVaiwan
• :
https://www.who.int/ith/2020-24-01-outbreak-of-Pneumonia-caused-by-new-coronavirus/en/
• WHO: Regional Office for Europe: 2019-nCoV outbreak:first cases confirmed in Europe
http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/emergencies/pages/news/news/2020/01/2019-ncov-
outbreak-first-cases-confirmed-in-europe
• Press statement by KCDC (in Korean):
https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20501000000&bid=0015&list_no=365794&act=view
#
• Second Press statement by KCDC (in Korean):
https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20501000000&bid=0015&list_no=365805&act=view
#
• Wuhan Municipal Health Commission’s briefing on the pneumonia epidemic situation, (in
Chinese):
http://wjw.wuhan.gov.cn/front/web/list2nd/no/710
• Disease outbreak news, Novel Coronavirus:
https://www.who.int/csr/don/en/
• Thailand Ministry of Public Health situation update on novel coronavirus (in Thai):
https://ddc.moph.go.th/viralpneumonia/index.html
• Press statement by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan on 16 January 2020 (in Japanese):
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_08906.html
• Press statement by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan on 6 January 2020 (in Japanese):
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_08767.html
• Notice sent out from Health and Food Safety Planning Division, Quarantine Station Operation
Management Office (in Japanese):
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000582967.pdf
▪ Situation report by WHO on Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
• CDC press release. First Travel-related Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Detected in United States
https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020/p0121-novel-coronavirus-travel-case.html
• Hong Kong SAR Department of Health, Press Release
https://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/202001/23/P2020012300970.htm
• Epidemic Prevention Measures, Macau SAR Health Bureau
https://www.ssm.gov.mo/apps1/PreventWuhanInfection/ch.aspx#clg17048
• Press release on 23 January 2020, Ministry of Health Singapore.
https://www.moh.gov.sg/news-highlights/details/confirmed-imported-case-of-novel-coronavirus-
infection-in-singapore-multi-ministry-taskforce-ramps-up-precautionary-measures
• CDC press release. Second Travel-related Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Detected in United States
https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020/p0124-second-travel-coronavirus.html
• New South Wales Government: Health: Coronavirus cases confirmed in NSW
https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/news/Pages/20200125_03.aspx









