WHO Director-General Outside of China reiterated that countries should not give up on stopping the outbreak now 44 067 confirmed (6703 new) that WHO has characterized it as a pandemic.
A shift from containment to 1440 deaths (310 new) mitigation would be wrong and dangerous. 
This is a controllable pandemic.
For detailed information, please see here. areas (4 new)
• On 11 March, ICAO and WHO issued a joint statement to reminding all WHO RISK ASSESSMENT
stakeholders of the importance of existing regulations and guidance. For more
information, please see here. China Very High
Regional Level Very High
Global Level Very High
Figure 1. Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of COVID-19, 12 March 2020
SUBJECT IN FOCUS: Clinical Case Management- update
The Clinical Unit continues to convene clinicians around the globe, twice weekly by teleconference (COVID-19
Clinical Network) to share knowledge and experiences from clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients and highlight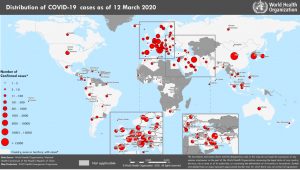
operational challenges and technical questions. There are over 30 countries represented on this call.
The major clinical challenge reported is the severity of the disease. A recent surge in critically ill patients requiring
mechanical ventilation has strained some health systems and exhausted biomedical supplies and staff. This has
highlighted the need to better support health systems become ready for such a surge in cases. Thus, the team
alongside our logistic colleagues and partners are developing a Clinical Concept of Operations intended to guide
countries with surge decision -making, and tools to accelerate the availability of oxygen and biomedical equipment.
In addition, the Clinical unit is regularly updating other products for clinical case management:
• The updated Clinical Management Guidance for COVID-19. This will include more detailed information
about the care of patients with mild and severe illness, young children, pregnant and postpartum women
and information about breastfeeding. To be released on 13 March 2020.
• The WHO Clinical Care Training materials continue to be available on openwho.org. This covers an approach
to clinical care from pre-triage/triage, diagnosis/testing and critical care interventions, such as lung
protective ventilation.
• The Global COVID-19 Clinical Data Platform continues to collect core clinical data from hospitalized patients
to inform understanding of clinical natural history and severity.
SURVEILLANCE
Table 1. Confirmed and suspected cases of COVID-19 acute respiratory disease reported by provinces, regions and
cities in China, Data as of 12 March 2020
Province/ In last 24 hours Cumulative
Population
Region/ Confirmed
(10,000s) Suspected Confirmed
City cases Deaths Deaths
cases cases
Hubei 5917 8 2 10 67781 3056
Guangdong 11346 3 1 0 1356 8
Henan 9605 1 0 0 1273 22
Zhejiang 5737 0 0 0 1215 1
Hunan 6899 0 0 0 1018 4
Anhui 6324 0 0 0 990 6
Jiangxi 4648 0 0 0 935 1
Shandong 10047 1 0 0 760 6
Jiangsu 8051 0 0 0 631 0
Chongqing 3102 0 0 0 576 6
Sichuan 8341 0 0 0 539 3
Heilongjiang 3773 0 0 0 482 13
Beijing 2154 0 5 0 435 8
Shanghai 2424 0 19 0 344 3
Hebei 7556 0 0 0 318 6
Fujian 3941 0 0 0 296 1
Guangxi 4926 0 0 0 252 2
Shaanxi 3864 0 0 1 245 2
Yunnan 4830 0 1 0 174 2
Hainan 934 0 1 0 168 6
Guizhou 3600 0 0 0 146 2
Tianjin 1560 0 4 0 136 3
Shanxi 3718 0 0 0 133 0
Hong Kong SAR 745 9 0 0 129 3
Gansu 2637 2 0 0 127 2
Liaoning 4359 0 0 0 125 1
Jilin 2704 0 0 0 93 1
Xinjiang 2487 0 0 0 76 3
Ningxia 688 0 0 0 75 0
Inner Mongolia 2534 0 0 0 75 1
Taipei and environs 2359 2 0 0 49 1
Qinghai 603 0 0 0 18 0
Macao SAR 66 0 0 0 10 0
Xizang 344 0 0 0 1 0
Total 142823 26 33 11 80981 3173
Table 2. Countries, territories or areas outside China with reported laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases and
deaths. Data as of 12 March 2020*
Total Total Total Days since last
Reporting Country/ Total Transmission
confirmed confirmed new reported case
Territory/Area† ‡ deaths classification§
cases new cases deaths
Western Pacific Region
Republic of Korea 7869 114 66 6 Local transmission 0
Japan 620 52 15 3 Local transmission 0
Singapore 178 12 0 0 Local transmission 0
Malaysia 129 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Australia 122 10 3 0 Local transmission 0
Philippines 52 3 2 1 Local transmission 0
Viet Nam 39 4 0 0 Local transmission 0
Brunei Darussalam 12 11 0 0 Local transmission 0
New Zealand 5 0 0 0 Local transmission 5
Cambodia 3 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Mongolia 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 2
Territories**
French Polynesia 1 1 0 0 Imported cases only 0
European Region
Italy 12462 2313 827 196 Local transmission 0
France 2269 495 48 15 Local transmission 0
Spain 2140 501 48 12 Local transmission 0
Germany 1567 271 3 1 Local transmission 0
Switzerland 645 154 4 1 Local transmission 0
Denmark 615 353 0 0 Local transmission 0
Netherlands 503 121 5 1 Local transmission 0
Sweden 461 135 0 0 Local transmission 0
The United Kingdom 460 87 6 0 Local transmission 0
Belgium 314 47 0 0 Local transmission 0
Austria 302 120 0 0 Local transmission 0
Norway 277 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Greece 98 9 1 1 Local transmission 0
Czechia 94 33 0 0 Local transmission 0
Israel 75 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
San Marino 63 0 2 0 Local transmission 1
Iceland 61 0 0 0 Local transmission 2
Slovenia 57 26 0 0 Local transmission 0
Romania 48 23 0 0 Local transmission 0
Poland 44 22 0 0 Local transmission 0
Ireland 43 9 1 1 Local transmission 0
Portugal 41 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Finland 40 0 0 0 Local transmission 2
Georgia 23 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Russian Federation 20 13 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Serbia 19 7 0 0 Local transmission 0
Luxembourg 17 12 0 0 Local transmission 0
Croatia 16 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Latvia 16 8 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Estonia 13 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Hungary 13 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Belarus 12 3 0 0 Local transmission 0
Albania 10 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Slovakia 10 3 0 0 Local transmission 0
Azerbaijan 9 0 0 0 Imported cases only 5
Bulgaria 7 1 1 1 Local transmission 0
North Macedonia 7 0 0 0 Local transmission 2
Cyprus 6 4 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Malta 6 2 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Bosnia and
Herzegovina 4 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Republic of Moldova 4 1 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Lithuania 3 2 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Andorra 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 9
Armenia 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 10
Holy See 1 0 0 0 Under investigation 6
Liechtenstein 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 6
Monaco 1 0 0 0 Under investigation 11
Turkey 1 1 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Ukraine 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 8
**
Territories
Faroe Islands 2 0 0 0 Imported cases only 3
Gibraltar 1 0 0 0 Under investigation 8
Guernsey 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 2
South-East Asia Region
India 73 13 0 0 Local transmission 0
Thailand 70 11 1 0 Local transmission 0
Indonesia 34 7 1 0 Local transmission 0
Maldives 8 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Bangladesh 3 0 0 0 Local transmission 3
Sri Lanka 2 1 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Bhutan 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 6
Nepal 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 48
Eastern Mediterranean Region
Iran (Islamic Republic
of) 9000 958 354 63 Local transmission 0
Qatar 262 238 0 0 Local transmission 0
Bahrain 189 79 0 0 Local transmission 0
Kuwait 80 11 0 0 Local transmission 0
United Arab Emirates 74 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Iraq 70 9 7 1 Local transmission 0
Egypt 67 8 1 0 Local transmission 0
Lebanon 66 25 3 2 Local transmission 0
Saudi Arabia 21 1 0 0 Local transmission 0
Pakistan 19 3 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Oman 18 0 0 0 Imported cases only 2
Afghanistan 7 3 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Tunisia 6 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Morocco 5 2 1 0 Local transmission 0
Jordan 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 9
**
Territories
occupied Palestinian
territory 30 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Region of the Americas
United States of
America 987 291 29 4 Local transmission 0
Canada 93 0 1 0 Local transmission 1
Brazil 52 18 0 0 Local transmission 0
Chile 23 6 0 0 Local transmission 0
Argentina 19 2 1 0 Imported cases only 0
Ecuador 17 2 0 0 Local transmission 0
Peru 17 6 0 0 Local transmission 0
Costa Rica 13 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Mexico 11 4 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Panama 10 2 1 0 Local transmission 0
Colombia 9 6 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Dominican Republic 5 0 0 0 Imported cases only 2
Paraguay 5 0 0 0 Local transmission 1
Bolivia (Plurinational
State of) 2 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Honduras 2 2 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Jamaica 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Territories**
French Guiana 5 0 0 0 Imported cases only 4
Martinique 3 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Saint Martin 2 0 0 0 Under investigation 9
Saint Barthelemy 1 0 0 0 Under investigation 9
African Region
Algeria 25 5 1 1 Local transmission 0
South Africa 13 6 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Senegal 4 0 0 0 Imported cases only 7
Burkina Faso 2 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Cameroon 2 0 0 0 Local transmission 5
Nigeria 2 0 0 0 Imported cases only 3
Côte d’Ivoire 1 1 0 0 Imported cases only 0
Democratic Republic
of the Congo 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 1
Togo 1 0 0 0 Imported cases only 5
Subtotal for all
regions 43371 6703 1433 310
International
conveyance 696 0 7 0 Local transmission 4
(Diamond Princess)
Grand total 44067 6703 1440 310
*
Numbers include both domestic and repatriated cases
†The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on
the part of WHO concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its
frontiers or boundaries. Dotted and dashed lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement.
‡Case classifications are based on WHO case definitions for COVID-19.
§Transmission classification is based on WHO analysis of available official data and may be subject to reclassification as additional data become
available. Countries/territories/areas experiencing multiple types of transmission are classified in the highest category for which there is
evidence; they may be removed from a given category if interruption of transmission can be demonstrated. It should be noted that even within
categories, different countries/territories/areas may have differing degrees of transmission as indicated by the differing numbers of cases and
other factors. Not all locations within a given country/territory/area are equally affected.
Terms:
– Community transmission is evidenced by the inability to relate confirmed cases through chains of transmission for a large number of cases, or by
increasing positive tests through sentinel samples (routine systematic testing of respiratory samples from established laboratories).
– Local transmission indicates locations where the source of infection is within the reporting location.
– Imported cases only indicates locations where all cases have been acquired outside the location of reporting.
– Under investigation indicates locations where type of transmission has not been determined for any cases.
– Interrupted transmission indicates locations where interruption of transmission has been demonstrated (details to be determined)
** “Territories” include territories, areas, overseas dependencies and other jurisdictions of similar status
Figure 2. Epidemic curve of confirmed COVID-19 cases reported outside of China (n= 44 067), by date of report and
WHO region through 12 March 2020
STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES
WHO’s strategic objectives for this response are to:
• Interrupt human-to-human transmission including reducing secondary infections among close contacts
and health care workers, preventing transmission amplification events, and preventing further
international spread*;
• Identify, isolate and care for patients early, including providing optimized care for infected patients;
• Identify and reduce transmission from the animal source;
• Address crucial unknowns regarding clinical severity, extent of transmission and infection, treatment
options, and accelerate the development of diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines;
• Communicate critical risk and event information to all communities and counter misinformation;
• Minimize social and economic impact through multisectoral partnerships.
*This can be achieved through a combination of public health measures, such as rapid identification, diagnosis
and management of the cases, identification and follow up of the contacts, infection prevention and control in
health care settings, implementation of health measures for travelers, awareness-raising in the population and
risk communication.
PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE
• To view all technical guidance documents regarding COVID-19, please go to this webpage.
• WHO has developed interim guidance for laboratory diagnosis, advice on the use of masks during home care and
in health care settings in the context of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak, clinical management,
infection prevention and control in health care settings, home care for patients with suspected novel
coronavirus, risk communication and community engagement and Global Surveillance for human infection with
novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV).
• WHO is working closely with International Air Transport Association (IATA) and have jointly developed a
guidance document to provide advice to cabin crew and airport workers, based on country queries. The
guidance can be found on the IATA webpage.
• WHO has been in regular and direct contact with Member States where cases have been reported. WHO is also
informing other countries about the situation and providing support as requested.
• WHO is working with its networks of researchers and other experts to coordinate global work on surveillance,
epidemiology, mathematical modelling, diagnostics and virology, clinical care and treatment, infection
prevention and control, and risk communication. WHO has issued interim guidance for countries, which are
updated regularly.
• WHO has prepared a disease commodity package that includes an essential list of biomedical equipment,
medicines and supplies necessary to care for patients with 2019-nCoV.
• WHO has provided recommendations to reduce risk of transmission from animals to humans.
• WHO has published an updated advice for international traffic in relation to the outbreak of the novel
coronavirus 2019-nCoV.
• WHO has activated the R&D blueprint to accelerate diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
• OpenWHO is an interactive, web-based, knowledge-transfer platform offering online courses to improve the
response to health emergencies. COVID-19 courses can be found here. Specifically, WHO has developed online
courses on the following topics: A general introduction to emerging respiratory viruses, including novel
coronaviruses (available in Arabic, English, French, Chinese, Spanish, Portuguese, and Russian); Critical Care of
Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (available in English and French); Health and safety briefing for respiratory
diseases – ePROTECT (available in English, French, and Russian); Infection Prevention and Control for Novel
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (available in English and Russian); and COVID-19 Operational Planning Guidelines and
COVID-19 Partners Platform to support country preparedness and response.
• WHO is providing guidance on early investigations, which are critical in an outbreak of a new virus. The data
collected from the protocols can be used to refine recommendations for surveillance and case definitions, to
characterize the key epidemiological transmission features of COVID-19, help understand spread, severity,
spectrum of disease, impact on the community and to inform operational models for implementation of
countermeasures such as case isolation, contact tracing and isolation. Several protocols are available here. One
such protocol is for the investigation of early COVID-19 cases and contacts (the “First Few X (FFX) Cases and
contact investigation protocol for 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection”). The protocol is designed to
gain an early understanding of the key clinical, epidemiological and virological characteristics of the first cases of
COVID-19 infection detected in any individual country, to inform the development and updating of public health
guidance to manage cases and reduce the potential spread and impact of infection.
RECOMMENDATIONS AND ADVICE FOR THE PUBLIC
If you are not in an area where COVID-19 is spreading or have not travelled from an area where COVID-19 is
spreading or have not been in contact with an infected patient, your risk of infection is low. It is understandable that
you may feel anxious about the outbreak. Get the facts from reliable sources to help you accurately determine your
risks so that you can take reasonable precautions (see Frequently Asked Questions). Seek guidance from WHO, your
healthcare provider, your national public health authority or your employer for accurate information on COVID-19
and whether COVID-19 is circulating where you live. It is important to be informed of the situation and take
appropriate measures to protect yourself and your family (see Protection measures for everyone).
If you are in an area where there are cases of COVID-19 you need to take the risk of infection seriously. Follow the
advice of WHO and guidance issued by national and local health authorities. For most people, COVID-19 infection
will cause mild illness however, it can make some people very ill and, in some people, it can be fatal. Older people,
and those with pre-existing medical conditions (such as cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease or
diabetes) are at risk for severe disease (See Protection measures for persons who are in or have recently visited (past
14 days) areas where COVID-19 is spreading).
CASE DEFINITIONS
WHO periodically updates the Global Surveillance for human infection with coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
document which includes case definitions.
For easy reference, case definitions are included below.
Suspect case
A. A patient with acute respiratory illness (fever and at least one sign/symptom of respiratory disease (e.g.,
cough, shortness of breath), AND with no other etiology that fully explains the clinical presentation AND a
history of travel to or residence in a country/area or territory reporting local transmission (See situation
report) of COVID-19 disease during the 14 days prior to symptom onset.
OR
B. A patient with any acute respiratory illness AND having been in contact with a confirmed or probable COVID-
19 case (see definition of contact) in the last 14 days prior to onset of symptoms;
OR
C. A patient with severe acute respiratory infection (fever and at least one sign/symptom of respiratory disease
(e.g., cough, shortness breath) AND requiring hospitalization AND with no other etiology that fully explains
the clinical presentation.
Probable case
A suspect case for whom testing for COVID-19 is inconclusive.
• Inconclusive being the result of the test reported by the laboratory
Confirmed case
A person with laboratory confirmation of COVID-19 infection, irrespective of clinical signs and symptoms.
• Information regarding laboratory guidance can be found here.








